Carrot
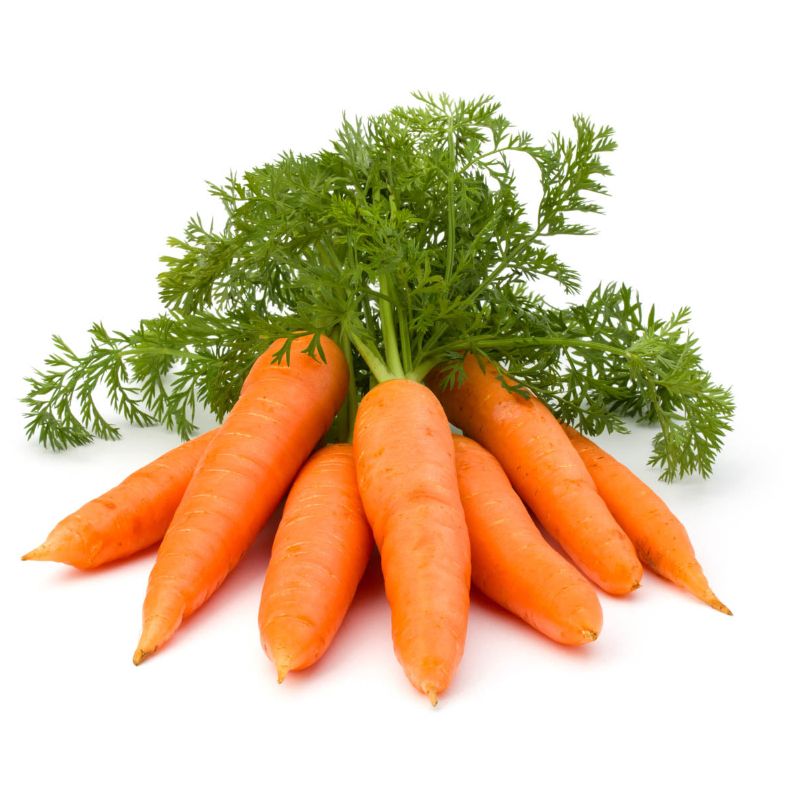
Carrots are a popular and nutritious root vegetable known for their vibrant orange color and sweet, earthy flavor. They belong to the Apiaceae family, which includes other vegetables like parsley, celery, and parsnips. Carrots are cultivated for their edible taproot, which is rich in vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber.
₹1,000.00
Carrot (Daucus carota)
Description: Carrots are a popular and nutritious root vegetable known for their vibrant orange color and sweet, earthy flavor. They belong to the Apiaceae family, which includes other vegetables like parsley, celery, and parsnips. Carrots are cultivated for their edible taproot, which is rich in vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber.
Plant Size: Carrot plants typically range from 12 to 24 inches in height, with feathery, fern-like foliage. The size of the taproot varies based on the carrot variety but is usually 6 to 12 inches in length.
Types: There are several types of carrots, including:
- Imperator: These are long and slender carrots, often used for fresh consumption and processing.
- Nantes: Shorter and broader than Imperator carrots, Nantes carrots are crisp and sweet.
- Chantenay: These carrots are shorter with broad shoulders, making them ideal for canning and cooking.
- Danvers: Known for their conical shape, Danvers carrots are great for both fresh and processing purposes.
Taste: Carrots have a sweet and earthy taste, with the sweetness more pronounced in varieties with a higher sugar content. They can be enjoyed raw as a snack or salad ingredient, or cooked in various dishes.
Color: While the most common color for carrots is orange, they can also be found in other colors such as purple, yellow, red, and white. Orange carrots are the most prevalent and well-known.
Soil Type for Growth: Carrots thrive in well-drained, sandy loam soil with good organic content. The soil should be loose to allow the roots to grow straight and deep. Carrots prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH (6.0-7.0).
Regions of Production: Carrots are grown worldwide, but major producing countries include China, Russia, the United States, and France. In India, the primary carrot-producing states are Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Himachal Pradesh.
Maturity Period: Carrots typically reach maturity in 60 to 80 days after planting, depending on the variety and growing conditions.
Environmental Conditions: Carrots thrive in cool to temperate climates. They require full sun exposure for at least 6 hours a day and can tolerate light frost. Adequate moisture is crucial during the growing season.
Physical Properties and Ingredients:
- Carrots are cylindrical or conical in shape, with a taproot that tapers to a point.
- They are composed of approximately 86-90% water.
- Carrots are rich in beta-carotene, which is converted to vitamin A in the body, as well as vitamins C and K, and various minerals like potassium and fiber.
Shelf Life After Harvesting: Carrots have a relatively long shelf life. When stored properly, they can last for several months. The shelf life depends on factors like temperature, humidity, and the presence of diseases or damage.
Storage Conditions: Carrots should be stored in a cool, dark place with a temperature of 32-40°F (0-4°C) and high humidity (90-95%). They can be stored in the refrigerator, preferably in a plastic bag to retain moisture.
Uses and Consumers: Carrots have a wide range of uses:
- They are commonly consumed raw as a snack, in salads, or as a garnish.
- Carrots are used in various culinary preparations, including soups, stews, stir-fries, and side dishes.
- They can be juiced for their health benefits.
- Carrots are also used in the production of baby food, carrot cake, and desserts.
- They are popular among health-conscious consumers due to their nutritional value, particularly their high vitamin A content.
Carrots are a versatile and nutritious vegetable enjoyed by people of all ages for their taste, health benefits, and culinary versatility.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.